The diagnosis of «bronchial asthma», determined to a child, does not complicate little person’s and his parents’ life for a long time. Proper treatment allows its normal development, active lifestyle, and with aging, attacks become milder, rarer, and often completely disappear.
- Inflammation develops due to the increased bronchi sensitivity to certain substances effects. Coughing and asthma attacks appear;
- It is important to identify factors that cause attacks (substance to which the child has an allergy or infections that provoke exacerbation). Sometimes, to relieve attacks it is simply necessary to remove the «inciting agent»;
- To prevent attack development or stop it, doctors prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs of different groups, including hormonal.

How does asthma in children occur?
The main asthma symptom is a chronical dry cough. In this case, body temperature does not increase and sputum does not discharge.
The second common symptom is an attack due to contact with certain substances to which a child has an allergy (allergens), or because of respiratory tract infections. During an attack, bronchi swell and fill with mucus viscous.
Depending on frequency and severity of attacks in children is divided into mild, moderately severe and severe. The attack begins with a cough, then dyspnea develops (lack of air).
Child’s breath is noisy, wheezing and can be heard even at a distance. Often attack is preceded by a runny nose, nasal stuffiness, itchy rash on the skin. Older children may complain of chest tightness and lack of air.
Causes of bronchial asthma
Asthma in children often develops on the background of hereditary predisposition to allergies, but the disease by itself can not be considered hereditary. There are two main precipitating factors for this disorder: allergy (predisposition to it is called atopy, and this type of asthma is called atopic), and inflammatory airway diseases (infectious type).
Disease type, caused by allergy, is more common. «Inciting agent» can be anything – food, dust, pollen, household chemicals, animal hair.
Sometimes asthma is a final type of allergic reactions, first child has urticaria, eczema (itchy vesiculation), hay fever (rhinitis), and only after some time, the body begins to react to the allergen with an attack.
Such attacks appear after frequent respiratory tract inflammations, mainly bronchitis, are less common. Then every time a new acute respiratory disease (ARD) episode cause attacks.
How to diagnose asthma in children?
The doctor collects detailed information about child’s life and how attacks develop. Sometimes during such a conversation, it’s already possible to suggest which allergen causes asthma.
Then comes the next step, when using a series of tests to identify an allergen, which causes attacks.
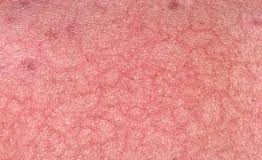
There is an old allergy determination method – skin test when solutions of different «inciting agents» are applied on the forearm, and as the result of these contacts with allergens skin redness appears. Be careful – this test cannot be held on the day of the attack, as it can provoke recrudescence, so it is better to take a blood test for allergens – it is safer and more informative.
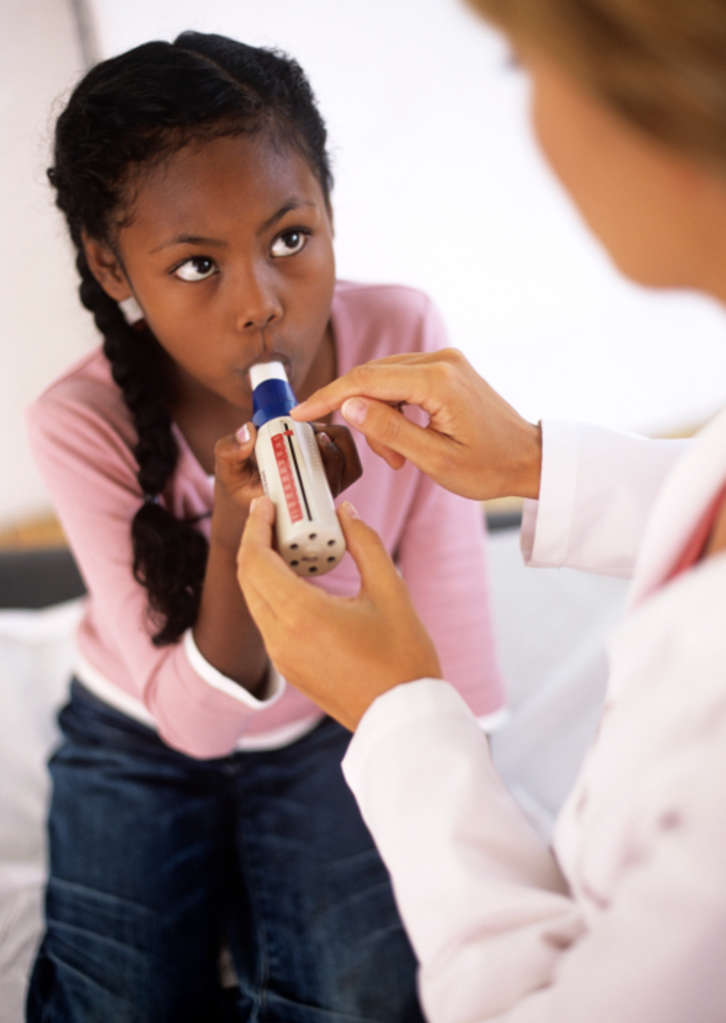
The next step is a necessary respiratory system disorder degree establishment. For this purpose, spirometry is applied (respiratory volume measurement).
The main indicators for spirometry:
- forced (i. e. made with effort) expiratory volume;
- forced vital capacity (volume of maximal inspiration plus volume of maximal expiration).
Unfortunately, asthma is often diagnosed too late, many months after symptoms onset. First, the diagnosis may sound like «obstructive bronchitis» («obstruction» means «blockage», in this case, bronchi lumen with mucus).
This happens partly due to the fact that parents perceive diagnosis of «bronchial asthma» as a sentence, meaning an obligatory disability. This may force a doctor to the last not make this «traumatic diagnosis», but prescribing the same drugs that are usually taken in this disease.
Treatment of bronchial asthma
For asthma treatment, it is often enough to remove allergen child’s surrounding. If this does not help, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory treatment.
Medications for the treatment are divided into two groups:
- those, that stop (neutralize) attack;
- those, that prevent its development.
For parents to consciously follow doctor’s recommendations, they need ask him, what each drug is used for. This will determine its dosing regimen.

In mild asthma, usual drugs of immune cells membrane stabilizers group (sodium cromoglicate). This drug does not work during an attack but does not allow it to develop. Under these drugs influence, immune cells do not release substances that cause inflammation and constrict bronchi.
In severe coarse to prevent attacks, a doctor prescribes hormones-corticosteroids (e. g. budesonide, fluticasone). Do not be afraid of these drugs, because they affect only bronchial mucous coat. In severe disease, the risk of side effects is much lower than a risk of disease.
To urgently relieve an asthma attack on a child, other drugs are used, that quickly cease bronchial spasm (salbutamol). They are usually produced in spray form, and every adult staying with a child must be able to provide correct inhalation.
It is important that parents of the child with asthma don’t consider him seriously ill, is possible let him lead an active lifestyle. When the child grows up, attacks will become rare, milder, and in many cases, they disappear at all.
Note that this perspective is not a reason to refuse treatment, including hormonal, if necessary. Each attack is a huge stress for the child, which must be eliminated by all means.